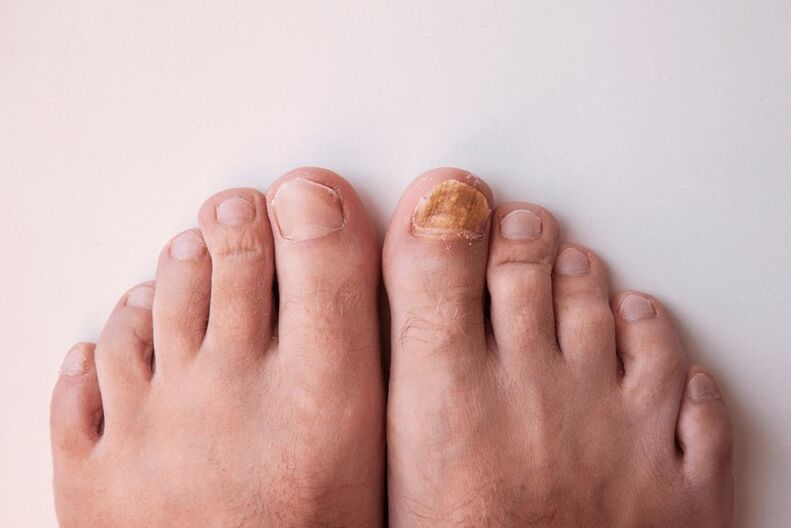
signs of fungal disease
- Color changes
- inflammation
- appearance of spots
- erosion
- deformation and thickening
Types of foot fungus
yeast-like fungal disease
Dermatomycosis
Mycosis
Forms of foot fungus
Squamous
Intermittent
Sweating disorder
Causes of foot fungus
- Excessive sweating or, conversely, more dry and flaky feet. These processes destroy the protective functions of skin cells.
- Anatomical features: narrowing between toes and deformation, flat feet.
- Problems with thermoregulation (maintaining a certain body temperature) and microcirculation (transporting biological fluids).
- Wounds, injuries that violate skin integrity. Through these injuries, infections often occur.
- There are diseases that reduce immunity or cause metabolic disorders (such as endocrine diseases, blood diseases, tumors, etc. ).
- Taking certain medications (antimicrobials, cytostatics, corticosteroids).
Diagnosis of foot fungus
- Assess the patient's chief complaints and presence of chronic conditions.
- Microscopic examination of affected skin and nail particles is performed.
- Culture seeding is the placement of pathogenic microorganisms in nutrient media for their propagation and subsequent accurate identification, as well as for the evaluation of the activity of antifungal drugs and the determination of the susceptibility of fungi to them.